Table of Contents
In today’s digital age, computer networks have become an integral part of our lives. From the internet to local area networks (LANs), computer networks are everywhere. However, for someone who is new to the world of computer networks, understanding the basics can be overwhelming. In this article, we will provide a beginner’s guide to computer networks, covering everything from the different types of networks to the components that make up a network.
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a group of interconnected devices that can communicate with each other. These devices can be computers, servers, printers, routers, switches, and other networking equipment. The purpose of a computer network is to share resources, such as data, files, and applications, among the devices connected to the network.
Types of Computer Networks
There are several types of computer networks, each with its own characteristics and uses. The most common types of computer networks are:
1. Local Area Network (LAN)

A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network infrastructure that interconnects devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or educational institution. LANs play a crucial role in facilitating seamless communication and resource sharing among devices connected to the network. By establishing a LAN, users can efficiently share resources such as printers, files, and internet connectivity, promoting collaboration and enhancing productivity within the local environment. Additionally, LANs often employ Ethernet or Wi-Fi technology to enable fast data transmission speeds, ensuring smooth and reliable communication between devices. With the evolution of LAN technology, including advancements like switches and routers, modern LANs have become increasingly sophisticated, offering enhanced security features and scalability to accommodate growing network demands. Whether it’s a small-scale home network or a complex corporate infrastructure, LANs remain a fundamental building block of today’s interconnected world.
2. Wide Area Network (WAN)
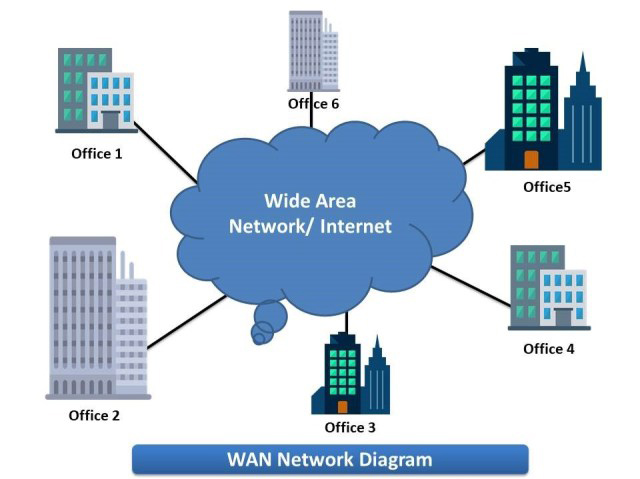
A WAN is a network that connects devices over a large geographical area, such as a city, country, or even the world. WANs are typically used to connect LANs and share resources among them.A Wide Area Network (WAN) serves as a crucial network infrastructure that connects devices spread across extensive geographical areas, spanning from local cities to entire countries and even global regions. Unlike Local Area Networks (LANs) that operate within a confined space, WANs enable seamless communication and resource sharing between geographically dispersed LANs. By establishing WAN connections, organizations can connect their branch offices, data centers, and remote locations to create a unified network environment. WANs utilize a variety of technologies, such as leased lines, MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching), and virtual private networks (VPNs), to ensure secure and efficient data transmission over long distances. The primary purpose of WANs is to facilitate collaboration, centralize resources, and enable organizations to operate seamlessly across diverse locations. Whether it’s sharing data, accessing centralized applications, or enabling real-time communication, WANs play a pivotal role in connecting LANs and extending network capabilities across vast geographical areas.
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
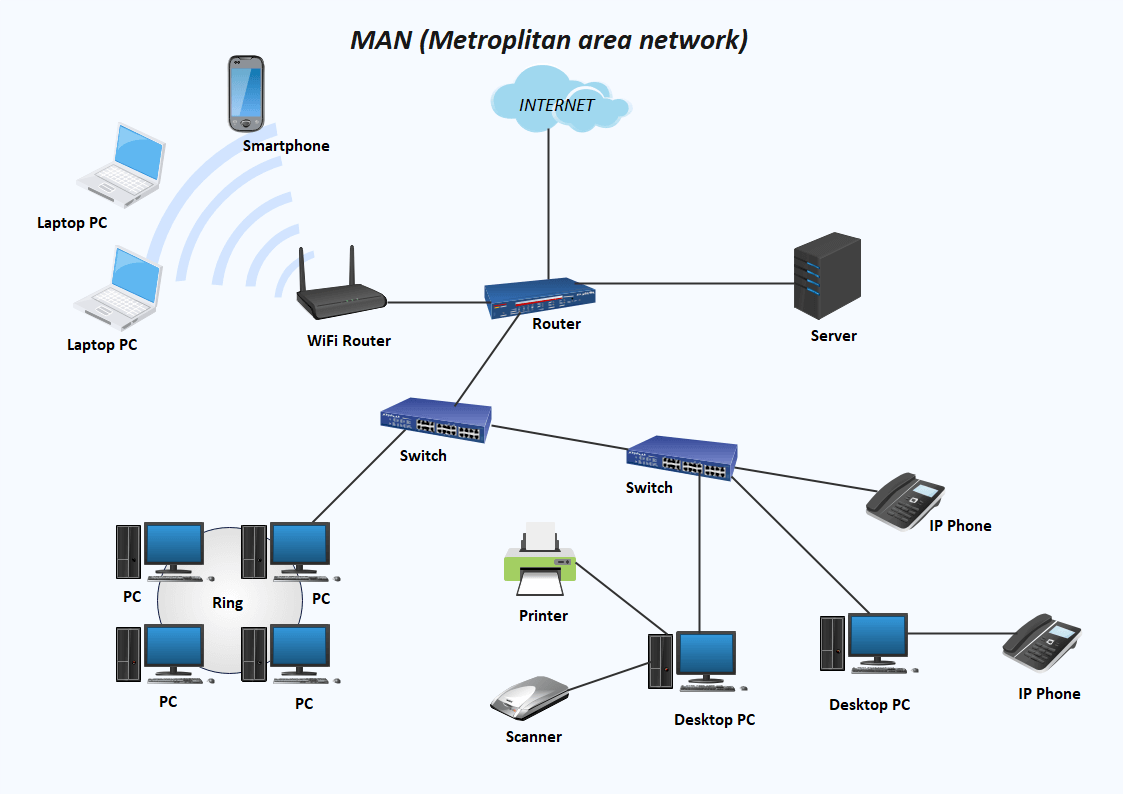
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a robust network infrastructure that interconnects devices within a specific metropolitan area, encompassing a city or town and its surrounding regions. MANs are designed to meet the networking needs of organizations that operate across multiple locations within a concentrated geographical area. By establishing a MAN, businesses can seamlessly connect their various offices, campuses, or branches, enabling efficient communication and resource sharing. MANs often utilize high-capacity fiber optic cables or other advanced networking technologies to ensure fast and reliable data transmission within the metropolitan region. These networks play a crucial role in supporting activities such as centralized data storage, collaborative work environments, and centralized access to shared applications and services. Whether it’s a university with multiple campuses, a government organization spanning different departments, or a large corporation with offices scattered across a city, MANs provide a reliable and scalable networking solution to streamline operations and enhance connectivity within a metropolitan area.
4. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)

A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a network infrastructure that enables wireless connectivity between devices within a limited geographical area, such as homes, offices, or educational institutions. WLANs utilize wireless communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi, to establish seamless connections between devices without the need for physical cables. This wireless network technology allows users to access the internet, share files, and communicate with other devices within the coverage area. WLANs are widely used to provide wireless internet access, enabling users to connect their smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other Wi-Fi-enabled devices to the network. With the convenience and flexibility of WLANs, users can enjoy mobility and freedom to access online resources and collaborate from anywhere within the network’s range. Whether it’s browsing the web, streaming media, or participating in online meetings, WLANs have become an essential part of modern connectivity, providing reliable wireless networking solutions for various environments.
Components of a Computer Network
A computer network is made up of several components, each with its own function. The most common components of a computer network are:
1. Network Interface Card (NIC)

A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a vital hardware component that enables devices to establish a connection and communicate within a network. Also known as a network adapter or network card, the NIC acts as an interface between the device and the network infrastructure. It facilitates the transmission and reception of data packets, allowing seamless communication with other devices on the network. The NIC is responsible for converting digital data from the device into a format that can be transmitted over the network, and vice versa. It plays a crucial role in enabling devices such as computers, servers, and laptops to access shared resources, exchange information, and participate in network activities. With various types of NICs available, including Ethernet, wireless, and Bluetooth adapters, each tailored to specific networking technologies, these components ensure the smooth flow of data and connectivity across the network.
2. Switch

A switch is a fundamental networking device that facilitates the connection and communication between devices within a network. Serving as a central hub, the switch allows multiple devices, such as computers, printers, and servers, to be connected together. By efficiently managing network traffic, a switch enables devices to exchange data and share resources seamlessly. Each device connected to the switch is assigned a unique network address, allowing for direct and efficient communication. With its intelligent forwarding capabilities, the switch analyzes incoming data packets and directs them to their intended recipients, optimizing network performance and reducing unnecessary traffic. This enables devices to interact, collaborate, and access shared resources, promoting efficient data sharing and enhanced productivity within the network environment. Switches are essential components in both small and large-scale networks, providing reliable and secure connectivity for various applications, from home networks to enterprise environments.
3. Router

A router is a crucial networking device that plays a vital role in connecting multiple networks together. It serves as a gateway, enabling devices from different networks to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. By examining the destination addresses of incoming data packets, the router determines the most efficient path for data transmission, ensuring that it reaches its intended destination. Routers use routing tables and protocols to make intelligent decisions about the best routes for data to travel across networks. They also provide network address translation (NAT) capabilities, allowing devices within a local network to share a single public IP address for internet connectivity. With its ability to interconnect networks and manage data traffic, routers enable efficient and secure communication between devices across different networks, whether it’s within a home, an organization, or across the internet.
4. Firewall

A firewall serves as a crucial security device designed to safeguard networks from unauthorized access and potential threats. It acts as a protective barrier between a network and external entities, monitoring all incoming and outgoing network traffic. By analyzing the data packets and comparing them against predefined security rules and policies, the firewall determines which traffic is permitted and which should be blocked. It effectively acts as a gatekeeper, filtering out any unauthorized or potentially malicious traffic from entering the network. This proactive approach helps to prevent unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, and other cybersecurity risks. Firewalls can be implemented at various network levels, including network perimeter, individual devices, or even within software applications, offering multi-layered protection. By enforcing strict security measures, firewalls play a critical role in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of a network, providing a robust defense against unauthorized access and ensuring a secure computing environment.
5. Server

A server is a powerful computer system that plays a central role in providing services to other devices on a network. It is designed to handle various tasks, such as storing and retrieving files, running applications, and delivering services like email, web hosting, or database management. Servers are equipped with robust hardware and software configurations to ensure high performance, reliability, and security. They are specifically optimized to handle heavy workloads, accommodate multiple simultaneous requests, and efficiently manage network resources. By acting as a centralized hub, servers enable seamless communication and collaboration among connected devices, enhancing productivity and facilitating efficient data management within the network environment.
6. Cable

A cable serves as a tangible connection medium that links devices together within a network infrastructure. It can take various forms, such as copper cables, fiber optic cables, or even wireless connections. Copper cables, known for their electrical conductivity, transmit data using electrical signals. Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, utilize thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light, enabling faster and more secure data transmission over longer distances. Wireless connections, leveraging radio waves or infrared signals, eliminate the need for physical cables altogether, providing flexibility and mobility. Regardless of the type, cables play a crucial role in establishing reliable and efficient communication pathways, facilitating the seamless transfer of data and information between networked devices.
Benefits of Computer Networks
There are several benefits of computer networks, including:
1. Resource Sharing
Computer networks enable the efficient sharing of valuable resources among devices, such as printers, files, and applications. By eliminating the need for individual devices to possess their own dedicated resources, networks promote cost-effectiveness and enhance efficiency. Instead of investing in separate printers, each device can access a shared printer, saving expenses and reducing maintenance efforts. Similarly, files and applications can be centrally stored and accessed by authorized devices, fostering collaboration and streamlining workflows. Through the power of networked connectivity, organizations and individuals can optimize resource utilization, maximize productivity, and achieve significant cost savings.
2. Communication
Computer networks facilitate seamless communication and foster enhanced collaboration among devices, offering a multitude of benefits for organizations with distributed locations or remote workforce. By enabling devices to connect and interact, networks empower teams to share information, exchange ideas, and work together in real-time regardless of physical distance. Remote workers can securely access shared resources, participate in virtual meetings, and contribute to projects, promoting productivity and agility. Moreover, networked communication ensures efficient coordination and timely decision-making, leading to streamlined workflows and optimized outcomes. Whether it’s file sharing, video conferencing, or instant messaging, computer networks play a vital role in creating a connected ecosystem that drives effective collaboration, boosts productivity, and empowers organizations to thrive in a digital landscape.
3. Centralized Management
Computer networks provide the advantage of centralized resource and device management, simplifying the administration and upkeep of the network infrastructure. With a centralized approach, network administrators can efficiently control and monitor various resources, such as servers, storage devices, and network devices, from a single management interface. This centralized management streamlines tasks like software updates, security configurations, and troubleshooting, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced operational costs. Additionally, it allows for better utilization of resources, as administrators can allocate and reallocate them based on demand, optimizing the network’s performance. By enabling centralized management, computer networks enable organizations to streamline their operations, enhance productivity, and ensure the smooth functioning of their network ecosystem.
4. Security
Computer networks offer the advantage of centralized security management, enhancing the overall protection of the network. Through a centralized approach, security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and access control mechanisms can be implemented and managed effectively. This ensures consistent and uniform security policies across all devices and network segments, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious activities. Network administrators can monitor network traffic, detect and respond to security threats promptly, and apply security patches and updates centrally. This centralized security management approach strengthens the network’s resilience and safeguards critical resources and data against potential vulnerabilities. By bolstering security measures through centralized management, computer networks provide organizations with increased confidence in the protection of their network infrastructure and sensitive information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, computer networks are an essential part of our digital lives. Understanding the basics of computer networks is important for anyone who wants to use them effectively. In this article, we have provided a beginner’s guide to computer networks, covering the different types of networks, the components that make up a network, and the benefits of computer networks. By understanding these basics, you can make the most of computer networks and improve your productivity and efficiency.

